
Eliminative materialism (also called eliminativism) is a materialist position in the philosophy of mind. Its primary claim is that people's common-sense understanding of the mind (or folk psychology) is false and that certain classes of mental states that most people believe in do not exist. Some eliminativists argue that no coherent neural basis will be found for many everyday psychological concepts such as belief or desire, since they are poorly defined. Rather, they argue that psychological concepts of behaviour and experience should be judged by how well they reduce to the biological level.[1] Other versions entail the non-existence of conscious mental states such as pain and visual perceptions.[2]
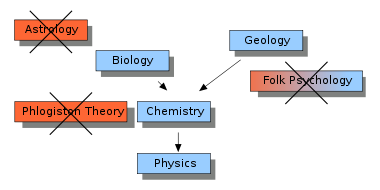
Eliminativism about a class of entities is the view that that class of entities does not exist.[3] For example, all forms of materialism are eliminativist about the soul; modern chemists are eliminativist about phlogiston; and modern physicists are eliminativist about the existence of luminiferous aether. Eliminative materialism is the relatively new (1960s-70s) idea that certain classes of mental entities that commonsense takes for granted, such as beliefs, desires, and the subjective sensation of pain, do not exist.[4][5] The most common versions are eliminativism about propositional attitudes, as expressed by Paul and Patricia Churchland,[6] and eliminativism about qualia (subjective experience), as expressed by Daniel Dennett and Georges Rey.[2]
Various arguments have been put forth both for and against eliminative materialism over the last forty years. Most of the arguments in favor of the view are based on the assumption that people's commonsense view of the mind is actually an implicit theory. It is to be compared and contrasted with other scientific theories in its explanatory success, accuracy, and ability to allow people to make correct predictions about the future. Eliminativists argue that, based on these and other criteria, commonsense "folk" psychology has failed and will eventually need to be replaced with explanations derived from the neurosciences. These philosophers therefore tend to emphasize the importance of neuroscientific research as well as developments in artificial intelligence to sustain their thesis.
Philosophers who argue against eliminativism may take several approaches. Simulation theorists, like Robert Gordon[7] and Alvin Goldman[8] argue that folk psychology is not a theory, but rather depends on internal simulation of others, and therefore is not subject to falsification in the same way that theories are. Jerry Fodor, among others,[9] argues that folk psychology is, in fact, a theory and a successful, even indispensable, one. Another view is that since eliminativism assumes the existence of the beliefs and other entities it seeks to "eliminate", it must be self-refuting.[10]
Contents[hide] |
Eliminativism maintains that the common-sense understanding of the mind is mistaken, and that the neurosciences will one day reveal that the mental states that are talked about in every day discourse, using words such as "intend", "believe", "desire", and "love", do not refer to anything real. Because of the inadequacy of natural languages, people mistakenly think that they have such beliefs and desires.[1] Some eliminativists, such as Frank Jackson, claim that consciousness does not exist except as an epiphenomenon of brain function; others, such as Georges Rey, claim that the concept will eventually be eliminated as neuroscience progresses.[2][11] Consciousness and folk psychology are separate issues and it is possible to take an eliminative stance on one but not the other.[3] The roots of eliminativism go back to the writings of Wilfred Sellars, W.V. Quine, Paul Feyerabend, and Richard Rorty.[4][5][12] The term "eliminative materialism" was first introduced by James Cornman in 1968 while describing a version of physicalism endorsed by Rorty. The later Ludwig Wittgenstein was also an important inspiration for eliminativism, particularly with his attack on "private objects" as "grammatical fictions".[3]
Early eliminativists such as Rorty and Feyerabend often confused two different notions of the sort of elimination that the term "eliminative materialism" entailed. On the one hand, they claimed, the cognitive sciences that will ultimately give people a correct account of the workings of the mind will not employ terms that refer to common-sense mental states like beliefs and desires; these states will not be part of the ontology of a mature cognitive science.[4][5] But critics immediately countered that this view was indistinguishable from the identity theory of mind.[1][13] Quine himself wondered what exactly was so eliminative about eliminative materialism after all:
| “ | Is physicalism a repudiation of mental objects after all, or a theory of them? Does it repudiate the mental state of pain or anger in favor of its physical concomitant, or does it identify the mental state with a state of the physical organism (and so a state of the physical organism with the mental state)? [14] | ” |
On the other hand, the same philosophers also claimed that common-sense mental states simply do not exist. But critics pointed out that eliminativists could not have it both ways: either mental states exist and will ultimately be explained in terms of lower-level neurophysiological processes or they do not.[1][13] Modern eliminativists have much more clearly expressed the view that mental phenomena simply do not exist and will eventually be eliminated from people's thinking about the brain in the same way that demons have been eliminated from people's thinking about mental illness and psychopathology.[3]
While it was a minority view in the 1960s, eliminative materialism gained prominence and acceptance during the 1980s.[15] Proponents of this view, such as B.F. Skinner, often made parallels to previous pseudoscientific theories (such as that of the the four humours, the phlogiston theory of combustion, and the vital force theory of life) that have all been successfully eliminated in attempting to establish their thesis about the nature of the mental. In these cases, science has not produced more detailed versions or reductions of these theories, but rejected them altogether as obsolete. Behaviorists argued that folk psychology is already obsolete and should be replaced by descriptions of stimulus and response patterns.[16] Such views were eventually abandoned. Patricia and Paul Churchland argued that folk psychology will be gradually replaced as neuroscience matures.[15]
Eliminativism is not only motivated by philosophical considerations, but is also a prediction about what form future scientific theories will take. Eliminativist philosophers therefore tend to be concerned with the data coming from the relevant brain and cognitive sciences.[17] In addition, because eliminativism is essentially predictive in nature, different theorists can, and often do, make different predictions about which aspects of folk psychology will be eliminated from folk psychological vocabulary. None of these philosophers are eliminativists "tout court".[18][19][20]
Today, the eliminativist view is most closely associated with the philosophers Paul and Patricia Churchland, who deny the existence of propositional attitudes (a subclass of intentional states), and with Daniel Dennett, who is generally considered to be an eliminativist about qualia and phenomenal aspects of consciousness. One way to summarize the difference between the Churchlands's views and Dennett's view is that the Churchlands are eliminativists when it comes to propositional attitudes, but reductionists concerning qualia, while Dennett is a reductionist with respect to propositional attitudes, and an eliminativist concerning qualia.[20][21][22]
Eliminativists such as Paul and Patricia Churchland argue that folk psychology is a fully developed but non-formalized theory of human behavior. It is used to explain and make predictions about human mental states and behavior. This view is often referred to as the theory of mind or just simply theory-theory, for it is a theory which theorizes the existence of an unacknowledged theory. As a theory in the scientific sense, eliminativists maintain, folk psychology needs to be evaluated on the basis of its predictive power and explanatory success as a research program for the investigation of the mind/brain.[23][24]
Such eliminativists have developed different arguments to show that folk psychology is a seriously mistaken theory and needs to be abolished. They argue that folk psychology excludes from its purview or has traditionally been mistaken about many important mental phenomena that can, and are, being examined and explained by modern neurosciences. Some examples are dreaming, consciousness, mental disorders, learning processes, and memory abilities. Furthermore, they argue, folk psychology's development in the last 2,500 years has not been significant and it is therefore a stagnating theory. The ancient Greeks already had a folk psychology comparable to modern views. But in contrast to this lack of development, the neurosciences are a rapidly progressing science complex that, in their view, can explain many cognitive processes that folk psychology cannot.[17][25]
Folk psychology retains characteristics of now obsolete theories or legends from the past. Ancient societies tried to explain the physical mysteries of nature by ascribing mental conditions to them in such statements as "the sea is angry". Gradually, these everyday folk psychological explanations were replaced by more efficient scientific descriptions. Today, eliminativists argue, there is no reason not to accept an effective scientific account of people's cognitive abilities. If such an explanation existed, then there would be no need for folk-psychological explanations of behavior, and the latter would be eliminated the same way as the mythological explanations the ancients used.[26]
Another line of argument is the meta-induction based on what eliminativists view as the disastrous historical record of folk theories in general. Ancient pre-scientific "theories" of folk biology, folk physics, and folk cosmology have all proven to be radically wrong. Eliminativists argue the same in the case of folk psychology. There seems no logical basis, to the eliminativist, for making an exception just because folk psychology has lasted longer and is more intuitive or instinctively plausible than the other folk theories.[25] Indeed, the eliminativists warn, considerations of intuitive plausibility may be precisely the result of the deeply entrenched nature in society of folk psychology itself. It may be that people's beliefs and other such states are as theory-laden as external perceptions and hence intuitions will tend to be biased in favor of them.[18]
Much of folk psychology involves the attribution of intentional states (or more specifically as a subclass, propositional attitudes). Eliminativists point out that these states are generally ascribed syntactic and semantic properties. An example of this is the language of thought hypothesis, which attributes a discrete, combinatorial syntax and other linguistic properties to these mental phenomena. Eliminativists argue that such discrete and combinatorial characteristics have no place in the neurosciences, which speak of action potentials, spiking frequencies, and other effects which are continuous and distributed in nature. Hence, the syntactic structures which are assumed by folk psychology can have no place in such a structure as the brain.[17] Against this there have been two responses. On the one hand, there are philosophers who deny that mental states are linguistic in nature and see this as a straw man argument.[27][28] The other view is represented by those who subscribe to "a language of thought". They assert that the mental states can be multiply realized and that functional characterizations are just higher-level characterizations of what's happening at the physical level.[29][30]
It has also been urged against folk psychology that the intentionality of mental states like belief imply that they have semantic qualities. Specifically, their meaning is determined by the things that they are about in the external world. This makes it difficult to explain how they can play the causal roles that they are supposed to in cognitive processes.[31]
In recent years, this latter argument has been fortified by the theory of connectionism. Many connectionist models of the brain have been developed in which the processes of language learning and other forms of representation are highly distributed and parallel. This would tend to indicate that there is no need for such discrete and semantically-endowed entities as beliefs and desires.[32]
The thesis of eliminativism seems to be so obviously wrong to many critics, under the claim that people know immediately and indubitably that they have minds, that argumentation seems unnecessary. This sort of intuition pumping is illustrated by asking what happens when one asks oneself honestly if one has mental states.[33] Eliminativists object to such a rebuttal of their position by claiming that intuitions often are mistaken. Analogies from the history of science are frequently invoked to buttress this observation: it may appear obvious that the sun travels around the earth, for example, but for all its apparent obviousness this conception was proved wrong nevertheless. Similarly, it may appear obvious that apart from neural events there are also mental conditions. Nevertheless, this could equally turn out to be false.[18]
But even if one accepts the susceptibility to error of people's intuitions, the objection can be reformulated: if the existence of mental conditions seems perfectly obvious and is central in people's conception of the world, then enormously strong arguments are needed in order to successfully deny the existence of mental conditions. Furthermore these arguments, to be consistent, need to be formulated in a way which does not pre-suppose the existence of entities like "mental states", "logical arguments", and "ideas", otherwise they are self-contradictory.[34] Those who accept this objection say that the arguments in favor of eliminativism are far too weak to establish such a radical claim; therefore there is no reason to believe in eliminativism.[33]
Quine's strategy for replying to such "introspective" arguments was to suggest that one could account for the activities of introspection and science in appropriately sanitized terms, such as the replacement of "belief" by "dispositions to utter certain sentences in certain circumstances".[14] Sentences, on this view, are just sequences of certain sounds, and theories just sets of sentences.
Some philosophers, such as Paul Boghossian, have attempted to show that eliminativism is in some sense self-refuting, since the theory itself presupposes the existence of mental phenomena. If eliminativism is true, then the eliminativist must permit an intentional property like truth, supposing that in order to assert something one must believe it. Hence, for eliminativism to be asserted as a thesis, the eliminativist must believe that it is true; if that is the case, then there are beliefs and the eliminativist claim is false.[10][35]
Georges Rey and Michael Devitt reply to this objection by invoking deflationary semantic theories that avoid analysing predicates like "x is true" as expressing a real property. They are construed, instead, as logical devices so that asserting that a sentence is true is just a quoted way of asserting the sentence itself. To say, "'God exists' is true" is just to say, "God exists". This way, Rey and Devitt argue, insofar as dispositional replacements of "claims" and deflationary accounts of "true" are coherent, eliminativism is not self-refuting.[36]
Another problem for the eliminativist is the consideration that human beings undergo subjective experiences and, hence, their conscious mental states have qualia. Since qualia are generally regarded as characteristics of mental states, their existence does not seem to be compatible with eliminativism.[37] Eliminativists, such as Daniel Dennett and Georges Rey, respond by rejecting qualia.[38][39] This is seen to be problematic to opponents of eliminativists, since many claim that the existence of qualia seems perfectly obvious. Many philosophers consider the "elimination" of qualia implausible, if not incomprehensible. They assert that, for instance, the existence of pain is simply beyond denial.[37]
The classic refutation of this objection comes from Daniel Dennett. Admitting that the existence of qualia seems obvious, Dennett nevertheless states that "qualia" is a theoretical term from an outdated metaphysics stemming from Cartesian intuitions. He argues that a precise analysis shows that the term is in the long run empty and full of contradictions. The eliminativist's claim with respect to qualia is that there is no unbiased evidence for such experiences when regarded as something more than propositional attitudes.[20] Influenced by Ludwig Wittgenstein's Philosophical Investigations, Dennett and Rey have defended eliminativism about qualia, even when other portions of the mental are accepted.
Some philosophers simply argue that folk-psychology is a quite successful theory.[9][40][41] Simulation theorists doubt that people's understanding of the mental can be explained in terms of a theory at all. Rather they argue that people's understanding of others is based on internal simulations of how they would act and respond in similar situations.[7][8] Jerry Fodor is one of the objectors that believes in folk psychology's success as a theory, because it makes for an effective way of communication in everyday life that can be implemented with few words. Such an effectiveness could never be achieved with a complex neuroscientific terminology. Furthermore, the eliminativist's claim that folk psychology cannot explain phenomena such as mental disorders or many memory processes has become often the objector's premise, namely that it is not at all the task of folk-psychology to account for these phenomena.[9]
Philosophers such as Mary Midgley strongly criticize all forms of reductionism—of which eliminative materialism is an extreme form—as unjustified imperialism that tries to annex one subject into another with poor evidence. She suggests that the reduction of chemistry to physics is problematic and the reduction of biology to chemistry is impossible. She points to sentences like "John was allowed home from prison at last on Sunday" suggesting that this would be impossible to reduce to physical terms since the details of the physical movement are irrelevant to the meaning which depends on complex non-physical concepts.[42] Her stance is that "human beings are complex wholes, about which we know really very little" and that attempts to reduce this are naive, unjustified and doomed to failure. She also claims that Behaviourism proved to be a philosophical and scientific dead-end.[42]
| Western Philosophy 21st-century philosophy |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Full name | Patricia Smith Churchland |
| Born | July 16, 1943 Oliver, British Columbia, Canada |
| School/tradition | Analytic Philosophy |
| Main interests | Neurophilosophy Philosophy of mind Philosophy of science Medical and environmental ethics |
Patricia Smith Churchland (born July 16, 1943 in Oliver, British Columbia, Canada) is a Canadian-American philosopher working at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) since 1984. She is currently a professor at the UCSD Philosophy Department, an adjunct professor at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, and an associate of the Computational Neuroscience Laboratory (Sejnowski Lab) at the Salk Institute. She won a MacArthur prize in 1991. Educated at the University of British Columbia, the University of Pittsburgh, and the University of Oxford (B.Phil.). She taught philosophy at the University of Manitoba from 1969 to 1984 and is the wife of philosopher Paul Churchland.
Churchland has focused on the interface between neuroscience and philosophy. According to her, philosophers are increasingly realizing that to understand the mind one must understand the brain. She is associated with a school of thought called eliminativism or eliminative materialism, which argues that folk psychology concepts such as belief, free will, and consciousness will likely need to be revised as science understands more about the nature of brain function.
She was interviewed along with her husband Paul Churchland for the book Conversations on Consciousness by Susan Blackmore, 2006.
She attended and was a speaker at the Beyond Belief symposium on November 2006 and November 2007.
Contents[hide] |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Patricia Churchland |
| Wikiquote has a collection of quotations related to: Patricia Churchland |
|
|
This biography of a living person does not cite any references or sources. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living people that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately. (April 2009) Find sources: (Thomas Metzinger – news, books, scholar) |
Thomas Metzinger (born March 12, 1958) is a German philosopher. He currently holds the position of director of the theoretical philosophy group at the department of philosophy at the Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz and is an Adjunct Fellow at the Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies. From 2008 to 2009 he is a Fellow at the Wissenschaftskolleg zu Berlin.
He has been active since the early 1990s in the promotion of consciousness studies as an academic endeavour. As a co-founder, he has been particularly active in the organization of the Association for the Scientific Study of Consciousness (ASSC), and sat on the board of directors of that organisation from 1994 to 2007. Metzinger is director of the MIND group and has been president of the German cognitive science society from 2005 to 2007. In English he has published two edited works, Conscious Experience (1995), and Neural correlates of consciousness: empirical and conceptual issues (2000). The latter book arose out of the second ASSC meeting, for which he acted as local organizer.
In 2003 he published the monograph Being No One. In this book he argues that no such things as selves exist in the world: nobody ever had or was a self. All that exists are phenomenal selves, as they appear in conscious experience. He argues that the phenomenal self, however, is not a thing but an ongoing process; it is the content of a "transparent self-model."
Metzinger is praised for his grasp of the fundamental issues of neurobiology, consciousness and the relationship of mind and body. However, his views about the self are the subject of considerable controversy and ongoing debates.
His interests include:
In the new field of neuroethics Thomas Metzinger is engaged by supervising the neuroethics web portal.
In 2009 he has published a public book for a general audience, The Ego Tunnel (Basic Books, New York, ISBN 0-465-04567-7).
Jack Cohen, FIBiol (born 19 September 1933) is a British reproductive biologist also known for his popular science books and involvement with science fiction.
Contents[hide] |
He studied at University College, Hull obtaining a BSc (external degree of the University of London) in 1954.He obtained his PhD in Zoology at the same institution, (by then Hull University) in 1957. He went to the University of Birmingham for post-doctoral work, and was appointed Lecturer in the Department of Zoology and Comparative Physiology in 1959. He worked for a year at Harvard Medical School then returned to Birmingham as a Senior Lecturer in 1968, a position he held until 1987. His former students include Sir Paul Nurse winner of the 2001 Nobel Prize for Medicine, and Dr Arthur Jones, a proponent of intelligent design. In 1974 the University of Birmingham awarded him a DSc for his work.
During 1987 to 1989 he was Senior Embryological Advisor and Manager of Laboratories at the IVF/Infertility Clinic of a London private hospital. During 1995 to 1996 he was Visiting Professor at the Weizmann Institute, Israel. From 1996 to 2000 he was a consultant at the University of Warwick jointly to the Ecosystems Unit of the Biology Dept and the Mathematics Institute. He is currently an Honorary Professor at the Mathematics Institute of the University of Warwick and a Visiting Professor at Durham Business School.
He has published in prestigious journals such as Nature and written textbooks such as Living Embryos - an Introduction to the Study of Animal Development (1967) and Reproduction (1977). His theory of sperm redundancy[1] has been important in studies of fertility and treatment of infertility. He is a Fellow of the Institute of Biology.
Cohen has worked as a consultant for both science fiction television shows and science fiction novelists on how to construct plausible aliens. His collaborators and associated works include Anne McCaffrey for the Dragonriders of Pern; the Legacy of Heorot collaboration of Larry Niven, Jerry Pournelle and Steven Barnes; several works by Terry Pratchett; and David Gerrold, whom he helped to design the Chtorr ecology.
He has also collaborated with fellow University of Warwick researcher Ian Stewart to write deep books on epistemology, and the science of the Discworld.
Jack Cohen is a member of the high IQ society Mensa. He was one of the small group of British Mensans who persuaded science fiction author Isaac Asimov to visit the United Kingdom in June 1974.[1]
In 1999 Terry Pratchett made both Jack and Professor Ian Stewart "Honorary Wizards of the Unseen University" at the same ceremony at which the University of Warwick gave Terry Pratchett an honorary degree.
In 2009, he became a patron of the anti-circumcision charity NORM-UK.[2]
His hobbies, according to the author profiles in his books, include boomerang-throwing and keeping strange animals.
| Western Philosophy 21st-century philosophy |
|
|---|---|
| Full name | Paul Churchland |
| Born | October 21, 1942 |
| School/tradition | Analytic Philosophy |
| Main interests | Neurophilosophy Philosophy of science Philosophy of mind Artificial intelligence Epistemology |
| Notable ideas | Eliminative Materialism |
Paul Churchland is a philosopher noted for his studies in neurophilosophy and the philosophy of mind.[1] He is currently a Professor at the University of California, San Diego, where he holds the Valtz Chair of Philosophy.[2] Churchland holds a joint appointment with the Cognitive Science Faculty and the Institute for Neural Computation.[3] He earned his Ph.D. from the University of Pittsburgh in 1969 under the direction of Wilfrid Sellars.[4] Churchland is the husband of philosopher Patricia Churchland, and the father of two children.[5]
Contents[hide] |
Churchland began his professional career as an instructor at the University of Pittsburgh in 1969;[6] he also lectured at the University of Toronto from 1967-69.[7] In 1969, Churchland took a position at the University of Manitoba, where he would teach for fifteen years: as an assistant professor (69 - 74) and associate professor (74 - 79), and then as a full professor from 1979 - 1984.[8] Professor Churchland joined the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton in 1982, staying as a member until 1983.[9] He joined the faculty at the University of California, San Diego in 1983, serving as Department Chair from 1986 - 1990.[10]
Churchland has supervised a number of PhD students, including Matthew Brown, P.D. Magnus (now at the University at Albany), Philip Brey (now at the University of Twente).
Along with his wife, Churchland is a major proponent of eliminative materialism, which claims that everyday mental concepts such as beliefs, feelings and desires are theoretical constructs without coherent definition; hence we should not expect such concepts to be a necessary part of a scientific understanding of humans. Just as a modern understanding of science has no need for concepts such as luck or witchcraft to explain the world, Churchland argues that a future neuroscience is likely to have no need for "beliefs" or "feelings". Such concepts will be eliminated and in their place more precise objective phenomena, such as neurons and their interaction, should suffice. He points out that the history of science has seen many previous concepts discarded, such as phlogiston, caloric, the luminiferous ether, and vital forces.